By Dr. Athanasios Staveris-Polykalas
In an era where the final frontier has become the next frontier for global military dynamics, the strategic importance of space technologies in national security and defense cannot be overstated. As nations increasingly rely on space to enhance their military and strategic capabilities, those that fail to embrace space technologies find themselves facing multifaceted dangers. This article delves into the significant risks and vulnerabilities that countries face when they neglect the development and integration of space technologies into their security and defense frameworks.
Strategic Disadvantage and Global Isolation
One of the most immediate and severe consequences of not leveraging space technologies is the resultant strategic disadvantage on the global stage. Space-enabled capabilities such as satellite communications, reconnaissance, and missile warning systems offer unparalleled advantages in terms of information dominance, situational awareness, and global reach. Without these capabilities, nations are not only blind to the activities of potential adversaries but also to the dynamics of global crises that could impact national security.
This strategic disadvantage extends into diplomatic isolation. As alliances and partnerships increasingly depend on shared space capabilities and data, countries lacking in space technologies find themselves excluded from critical security coalitions and discussions. This isolation undermines their ability to influence international security policies and participate in collective defense mechanisms, leaving them vulnerable to coercion and external threats.
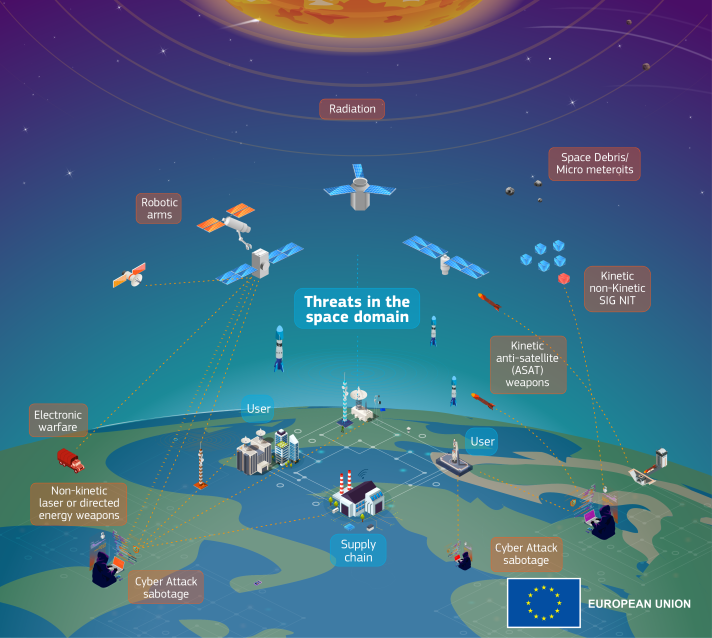
Increased Vulnerability to Attacks
The absence of space-based assets significantly increases a country’s vulnerability to both conventional and asymmetric threats. Satellite imagery and signals intelligence play crucial roles in early warning systems, detecting and tracking missile launches, troop movements, and other potential threats. Without these capabilities, nations are at a disadvantage in preemptively identifying and countering threats to their security.
Moreover, the reliance on terrestrial communication and navigation systems, which are more susceptible to disruption and attack, can cripple military operations and critical infrastructure. In contrast, space technologies provide resilient alternatives that can operate even when ground-based networks are compromised.
Dependence and Compromised Sovereignty
Countries that do not develop their own space capabilities often find themselves dependent on other nations or commercial entities for critical information and services. This dependence can compromise national sovereignty, as access to data and services may be constrained by the geopolitical interests of the provider. Furthermore, such reliance exposes countries to the risk of espionage and manipulation, as the control over the flow and integrity of the information remains with the external entity.
Economic and Technological Stagnation
The neglect of space technologies not only affects military and strategic capabilities but also impedes economic and technological development. The space industry drives innovation in numerous sectors, including telecommunications, navigation, and Earth observation, contributing significantly to national economies. Failure to invest in space technologies means missing out on the benefits of this high-growth sector, including job creation, technological advancements, and economic diversification.
Mitigating the Dangers through Global Cooperation and Policy Reforms
To mitigate these dangers, countries need to adopt comprehensive space policies that emphasize the development of indigenous space capabilities and the establishment of international partnerships. Collaborating with other nations and participating in multinational space projects can offer a pathway to acquiring space capabilities without the prohibitive costs of independent development.
Additionally, international norms and agreements play a crucial role in ensuring space remains a safe and sustainable environment for all. By engaging in diplomatic efforts to promote responsible behaviors in space, countries can contribute to global stability and security, even as they work to develop their own space capabilities.
Conclusion
The space domain is increasingly recognized as a critical theater for national security and global stability. As such, the failure to embrace space technologies poses significant risks, from strategic disadvantages and global isolation to increased vulnerabilities and economic stagnation. In addressing these challenges, nations must balance the development of indigenous capabilities with active participation in international space cooperation and governance. The future of national security is inexorably linked to space, and only by recognizing and acting on the imperative of space technologies can countries ensure their security, prosperity, and place in the international community.